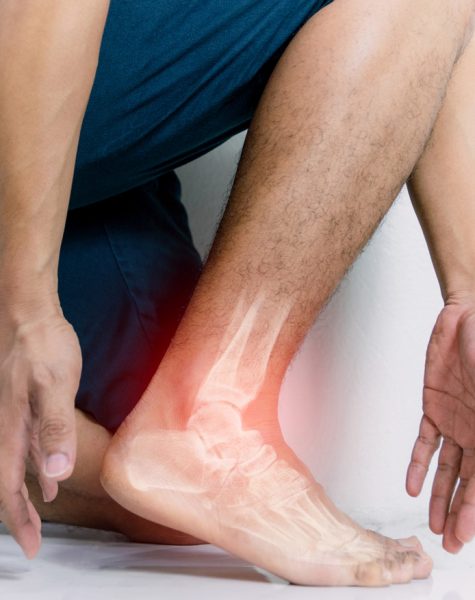
What is Post-Tib Tendonitis?
Post-Tib Tendonitis is a strain placed on the posterior tibial tendon. The posterior tibial tendon runs along the inside of the ankle and the foot. When there is post-tibial tendon disfunction, the tendon does not function to hold up the arch, resulting in flat feet. This can lead to heel pain, arch pain, plantar fasciitis, and/or heel spurs. With post-tib tendonitis, the pain will be more severe upon weight bearing, especially while walking or running.
Cause
Post-Tib Tendonitis occurs when the muscle is overused and the tendon (soft tissue) that connects the muscle to your bone is strained. Years of over-pronation (flat feet) can also lead to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. If you keep overusing the muscle, damage to the tendon builds up and tendonitis develops. At first, the pain or swelling may come and go quickly, but eventually, the problem may become more permanent.
What is Post-Tib Tendonitis?
Post-Tib Tendonitis is a strain placed on the posterior tibial tendon. The posterior tibial tendon runs along the inside of the ankle and the foot. When there is post-tibial tendon disfunction, the tendon does not function to hold up the arch, resulting in flat feet. This can lead to heel pain, arch pain, plantar fasciitis, and/or heel spurs. With post-tib tendonitis, the pain will be more severe upon weight bearing, especially while walking or running.
Cause
Post-Tib Tendonitis occurs when the muscle is overused and the tendon (soft tissue) that connects the muscle to your bone is strained. Years of over-pronation (flat feet) can also lead to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. If you keep overusing the muscle, damage to the tendon builds up and tendonitis develops. At first, the pain or swelling may come and go quickly, but eventually, the problem may become more permanent.
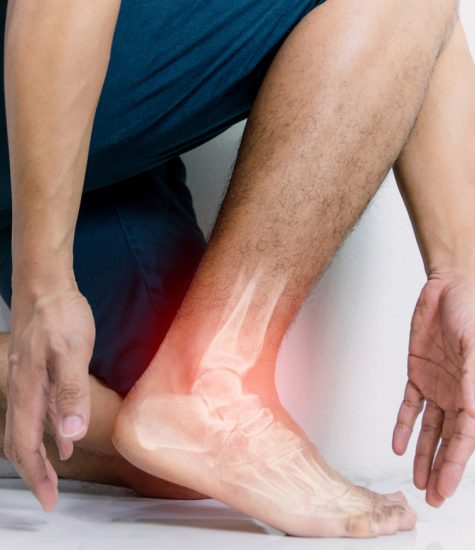

Treatment and Prevention
To treat post-tib tendonitis, you can reduce your symptoms by limiting activity to control the pain and swelling. Stay off your feet a few days, then slowly increase your activity. Rest allows the tissues in your foot to heal.
Conservative treatments (non-surgical treatments) include wearing a foot orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support to reduce strain on the post tibial tendon and prevent excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. The orthotic should also be designed with materials to comfort the foot and absorb shock.
Listed below are tips to prevent Post-Tib Tendonitis from recurring:
- Wear shoes that provide cushioning, support, and shock absorption
- Use orthotics with sufficient arch support that are constructed from shock-absorbing, cushioning materials
- Vary exercise routines; the variety will keep one set of muscles from being under continuous stress
Your podiatric physician/surgeon has been trained specifically and extensively in the diagnosis and treatment of all manners of foot conditions. This training encompasses all of the intricately related systems and structures of the foot and lower leg including neurological, circulatory, skin, and the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves.
Treatment and Prevention
To treat post-tib tendonitis, you can reduce your symptoms by limiting activity to control the pain and swelling. Stay off your feet a few days, then slowly increase your activity. Rest allows the tissues in your foot to heal.
Conservative treatments (non-surgical treatments) include wearing a foot orthotic with rearfoot posting and longitudinal arch support to reduce strain on the post tibial tendon and prevent excessive stretching of the plantar fascia. The orthotic should also be designed with materials to comfort the foot and absorb shock.
Listed below are tips to prevent Post-Tib Tendonitis from recurring:
- Wear shoes that provide cushioning, support, and shock absorption
- Use orthotics with sufficient arch support that are constructed from shock-absorbing, cushioning materials
- Vary exercise routines; the variety will keep one set of muscles from being under continuous stress
Your podiatric physician/surgeon has been trained specifically and extensively in the diagnosis and treatment of all manners of foot conditions. This training encompasses all of the intricately related systems and structures of the foot and lower leg including neurological, circulatory, skin, and the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, and nerves.

